What is climate change?

Definition: Climate change describes a change in the average conditions in a region, over a long period of time.
The climate on Earth has been changing ever since the Earth formed over 4.5 billion years ago. Until recently such changes have been caused by natural phenomenon like volcanic eruptions, solar activity and the regular changes in the Earth's orbit around the sun.
Historically, the Earth has warmed and cooled in a regular cycle; moving from an ice age to a warmer period, or vice versa, approximately every 100,000 years, as shown in Figure 1 part (A).
Since the 1800s, the global temperature has increased at a much faster rate, accelerating even more so in the past 30 years as Figure 1 part (B) shows. The blue line demonstrates what the surface temperature would be if only natural factors were observed. The brown line, which includes natural and human factors, demonstrates the temperature which was actually observed. Human factors such as burning fossil fuels have caused a much higher surface temperature.
2024 was the world's warmest year on record at 1.53°C above the long-term average.

Figure 1 - IPCC, 2021
Scientists unanimously agree that this global temperature change is due to human activity.
Carbon Dioxide

Figure 2 - NOAA Global Monitoring Laboratory
Since pre-industrial times, the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide has increased by 50%.
Human activities currently emit an estimated 37 billion tonnes of carbon each year.
Fossil Fuels - are natural fuels such as coal or gas, formed in the geological past from the remains of living organisms.
When fossil fuels are burned to create energy, they release carbon.
Energy Use in Sunderland (UK)
The leading causes of carbon emissions in Sunderland comes from domestic energy and transport.
Why are carbon dioxide increases leading to climate change?
Atmospheric Gases: Most of the Earth's atmosphere is made up of Oxygen and Nitrogen. Only a small percentage is made up of greenhouse gases (>1%), such as Carbon Dioxide, Methane and Nitrous Oxides.
Greenhouse Gases: A gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation (heat from the sun).
Greenhouse Effect: Greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere block heat from escaping. Human activities — such as burning fuel to power factories, cars and buses — are changing the natural greenhouse. These changes cause the atmosphere to trap more heat than it used to, leading to a warmer Earth, as shown in Figure 4. As well as the Earth getting hotter overall (Global Warming) the increase in global temperature is causing climates all over the world to change (Climate Change).
The atmospheric concentrations of CO2, methane and nitrous oxides have increased to levels unprecedented in at least the last 800,000 years.
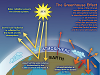
Figure 4 - IPCC, Working Group 1: The Physical Basis, 2007
Climate change effects in Sunderland
This Climate Report provides a summary of climate change effects in Sunderland. It uses scientific research to provide information to help plan for the future, enabling Sunderland to become more resilient to climate change.
Click on the link for the Met Office's Climate Report for Sunderland




